Basic D.C. Voltmeter
The basic d.c. voltmeter is nothing but a PMMC D'Arsonoval galvanometer. The resistance is required to be connected in series with the basic meter to use it as a voltmeter.
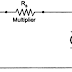
This series resistance is called a multiplier. The main function of the multiplier is to limit the current through the basic meter so that the meter current does not exceed the full scale deflection value. The voltmeter measures the voltage across the two points of a circuit or a voltage across circuit component. The basic d.c. voltmeter is shown in the Fig. 1.
 |
| Fig. 1 Basic of d.c. voltmeter |
The voltmeter must be connected across the two points or a component, to measure the potential difference, with the proper polarity.
The multiplier resistance can be calculated as:
Let Rm = Internal resistance of coil i.e. meter
Rs = series multiplier resistance
Im = full scale deflection current
V = full range voltage to be measured
From Fig 1, ... V = Im (Rm + Rs )
... V = ImRm + Im Rs
The multiplying factor for multiplier is the ratio of full range voltage to be measured and the drop across the basic meter.
Let v = drop across the basic meter = ImRm
Hence multiplier resistance can also be expressed as,
Rs = (m-1)
Basic D.C. Voltmeter
 Reviewed by haru
on
July 01, 2014
Rating:
Reviewed by haru
on
July 01, 2014
Rating:
 Reviewed by haru
on
July 01, 2014
Rating:
Reviewed by haru
on
July 01, 2014
Rating:










No comments