Relation between Charge and Applied Voltage
AS seen earlier, the charge on capacitor plates depends on the applied voltage. Let 'V' be the voltage applied to the capacitor and 'Q' be the charge accumulated on the capacitor plates, then mathematically, it can be written as,
The constant of proportionality 'C' is called capacitance of the capacitor, defined earlier.
From the above expression, the capacitance is defined as the ratio of charge acquired to attain the potential difference between the plates. It is the charge required per unit potential difference. It is measured in unit farads.
One farad capacitance is defined as the capacitance of a capacitor which requires a charge of one coulomb to establish a potential difference of one volt between its plates.
The capacitance is symbolically denoted as shown in the Fig 1.
For practical use, the farad is too large unit and hence, micro farad (µF), nano farad (nF) and pico farad (Pf) are commonly used.
Relation between Charge and Applied Voltage
 Reviewed by haru
on
April 08, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by haru
on
April 08, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by haru
on
April 08, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by haru
on
April 08, 2017
Rating:







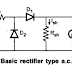
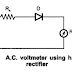


No comments